Introduction: The Art of War in Ancient Rome
Imagine a world where armies didn’t just clash on open fields but brought entire cities to their knees. Roman siege warfare was more than just a military tactic—it was a testament to their ingenuity, engineering, and unyielding ambition. Sieges were epic events that shaped the fate of empires, cities, and cultures. From towering siege engines to relentless strategies, the Romans mastered the art of breaking through walls. This article explores the strategies, technologies, and battles that made Roman siege warfare legendary.
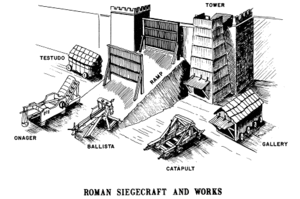
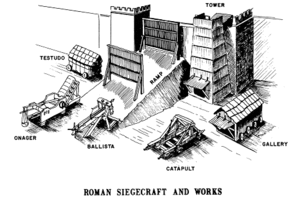
Roman siege engines in action – Source: Wikipedia
1. The Need for Siege Warfare: When Battles Turned to Walls
The Romans were known for their love of open battles, where discipline and formations often led to victory. However, when faced with fortified cities, they had to adapt. Siege warfare became essential for securing victory and asserting dominance. These battles were costly and time-consuming, but the Romans recognized their necessity. From Gaul to the Middle East, sieges became a critical tool in their expansion.
2. Engineering Marvels: The Tools of Destruction
The Romans weren’t just soldiers—they were engineers. Their siege engines were marvels of ancient technology. The ballista, a giant crossbow, could hurl massive projectiles with deadly accuracy. The onager, a type of catapult, was capable of smashing walls and spreading chaos. Siege towers, towering structures on wheels, allowed troops to scale walls while staying protected. These tools gave the Romans an edge, showcasing their unmatched engineering prowess.

Roman siege tower – Source: History Hit
3. Epic Battles: The Sieges That Shaped History
Some sieges stand out as turning points in history. The Siege of Alesia (52 BCE) saw Julius Caesar trap the Gallic leader Vercingetorix, securing Roman dominance in Gaul. The Siege of Jerusalem (70 CE) ended in the destruction of the Second Temple, a pivotal moment in Jewish history. And who could forget the Siege of Carthage (146 BCE), where Rome razed the city to the ground, symbolizing their ruthless determination. These battles weren’t just about conquest—they were about sending a message.
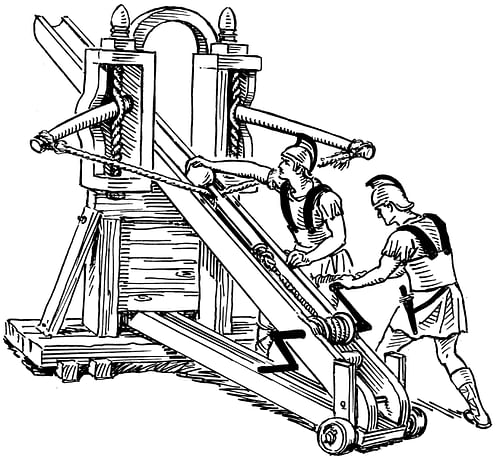
Roman siege warfare – Source: World History Encyclopedia
4. Cultural Impact: Sieges in Roman Identity
Sieges weren’t just military events; they became part of Roman culture. Stories of epic sieges were immortalized in literature, art, and history. The destruction of cities like Carthage and Jerusalem reinforced Roman dominance and left a lasting cultural legacy. These narratives shaped how the Romans saw themselves—as powerful, ingenious, and unyielding.
5. Legacy of Roman Siege Warfare: From Antiquity to the Modern Era
The influence of Roman siege warfare didn’t end with the fall of Rome. Their tactics and technologies inspired medieval and later military engineering. From castle fortifications to modern siege strategies, the lessons of Roman ingenuity continue to resonate. Their legacy is a reminder of the timeless importance of adaptability and innovation in warfare.
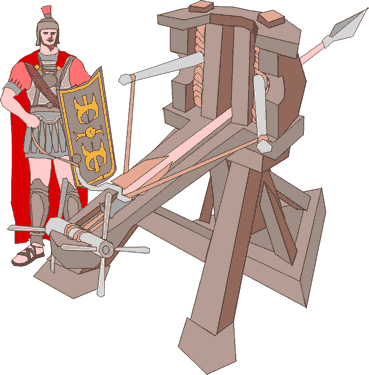
Roman siege machines – Source: HistoryLink101
Conclusion: The Enduring Epic of Roman Siege Warfare
Roman siege warfare was more than just a series of battles—it was an epic tale of strategy, technology, and conquest. From the engineering marvels that broke down walls to the sieges that shaped empires, the Romans left an indelible mark on history. Their legacy reminds us that even the most formidable walls can fall with the right mix of ingenuity and determination.
References:
Roman Siege Engines – Wikipedia – link
5 Important Roman Siege Engines – History Hit – link
Roman Siege Warfare – World History Encyclopedia – link
Roman Siege Machines – HistoryLink101 – link
Categories: Ancient Rome, History, Military, War History
Tags: ancient technology, Historical Battles, Military Strategy, Roman Empire, Siege Warfare
Religion: Paganism
Country of Origin: France, Israel, Italy, Tunisia
Topic: Roman Siege Warfare
Ethnicity: Roman