Introduction: The Epic Nature of Roman Siege Warfare
Imagine the year 52 BCE. Julius Caesar stands before the fortified walls of Alesia, surrounded by thousands of Roman soldiers. The air is thick with tension as the fate of an empire hangs in the balance. Roman siege warfare wasn’t just about brute force—it was an art form. These sieges were epic events that shaped history, combining strategy, engineering, and sheer determination. From Alesia to Jerusalem, the Romans mastered the art of conquest, leaving behind a legacy that still fascinates us today.
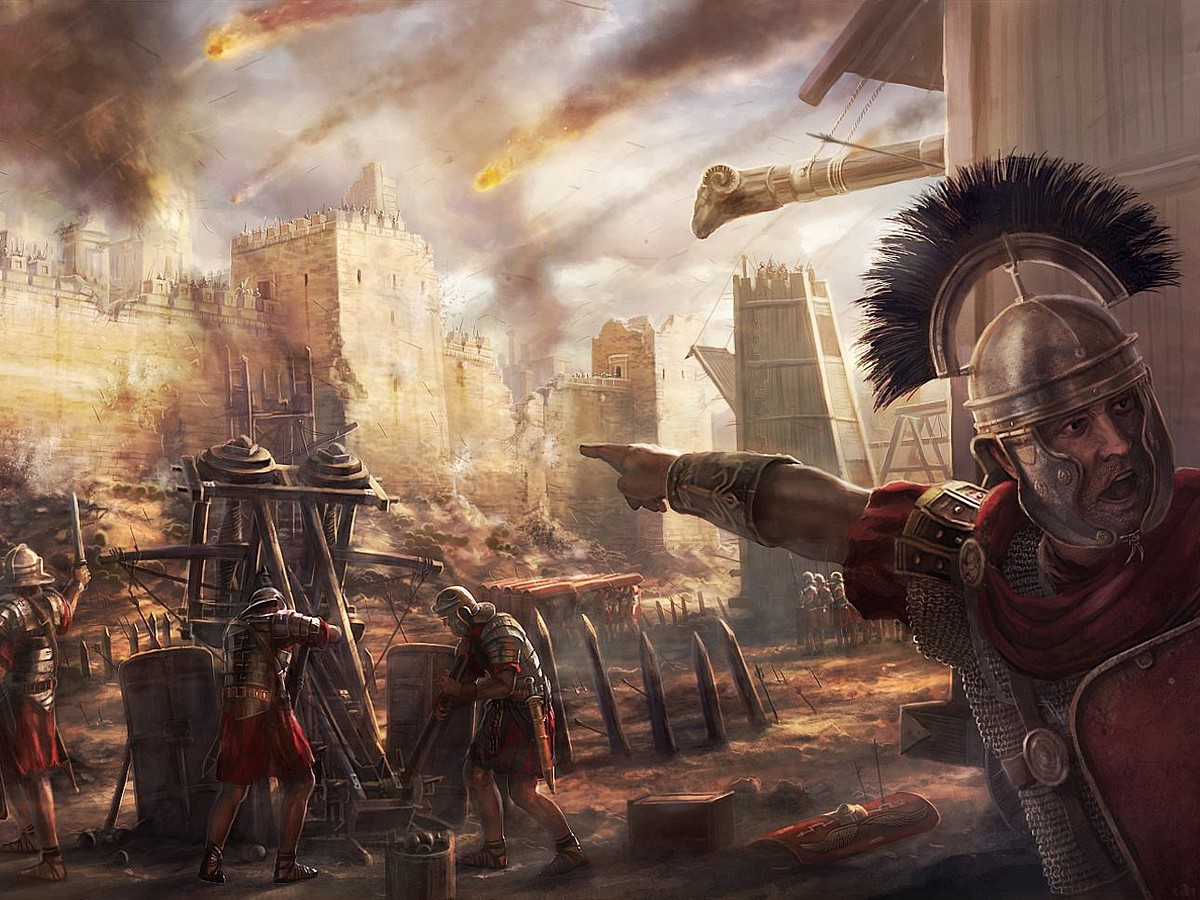

Credit: World History Encyclopedia
Historical Background: The Roots of Roman Siege Warfare
The Romans didn’t invent siege warfare, but they perfected it. Early Roman armies learned from their enemies, like the Greeks and Carthaginians, during conflicts such as the Punic Wars. Over time, they refined their tactics, turning sieges into a key tool for expansion. For example, during the Gallic Wars, Rome’s ability to besiege and conquer fortified cities like Alesia showcased their growing military dominance. These battles weren’t just about territory—they were about establishing Rome as an unstoppable force.
Credit: Wikipedia
Technological Advancements: Engineering the Art of Siege
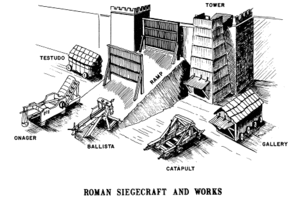
Roman siege warfare was as much about brains as it was about brawn. The Romans were master engineers, creating formidable siege engines like the ballista and onager. The ballista, a giant crossbow, could launch massive projectiles, while the onager, a type of catapult, could hurl stones to crush walls. These machines were game-changers, allowing the Romans to breach even the strongest defenses. Their ingenuity didn’t stop there—they also built siege towers, battering rams, and even underground tunnels to outsmart their enemies.

Credit: ABPosters
Cultural and Political Impact: The Consequences of Conquest
The success of Roman sieges didn’t just reshape maps—it transformed cultures. Cities that surrendered often retained some autonomy, while those that resisted faced destruction and enslavement. This approach sent a clear message: resistance was futile. Over time, conquered territories adopted Roman customs, laws, and languages, creating a unified empire. The cultural and political impact of these sieges was profound, laying the foundation for the Roman Empire’s enduring influence.

Credit: History Hit
Strategic Usage: Key Battles That Defined an Empire
Some sieges stand out as turning points in history. Take the Siege of Alesia, where Julius Caesar’s forces trapped the Gallic leader Vercingetorix. Using a double wall of fortifications, Caesar cut off supplies and reinforcements, forcing surrender. Similarly, the Siege of Jerusalem in 70 CE marked the end of Jewish resistance, solidifying Roman control over Judea. These battles weren’t just military victories—they were psychological triumphs that demonstrated Rome’s strategic brilliance.
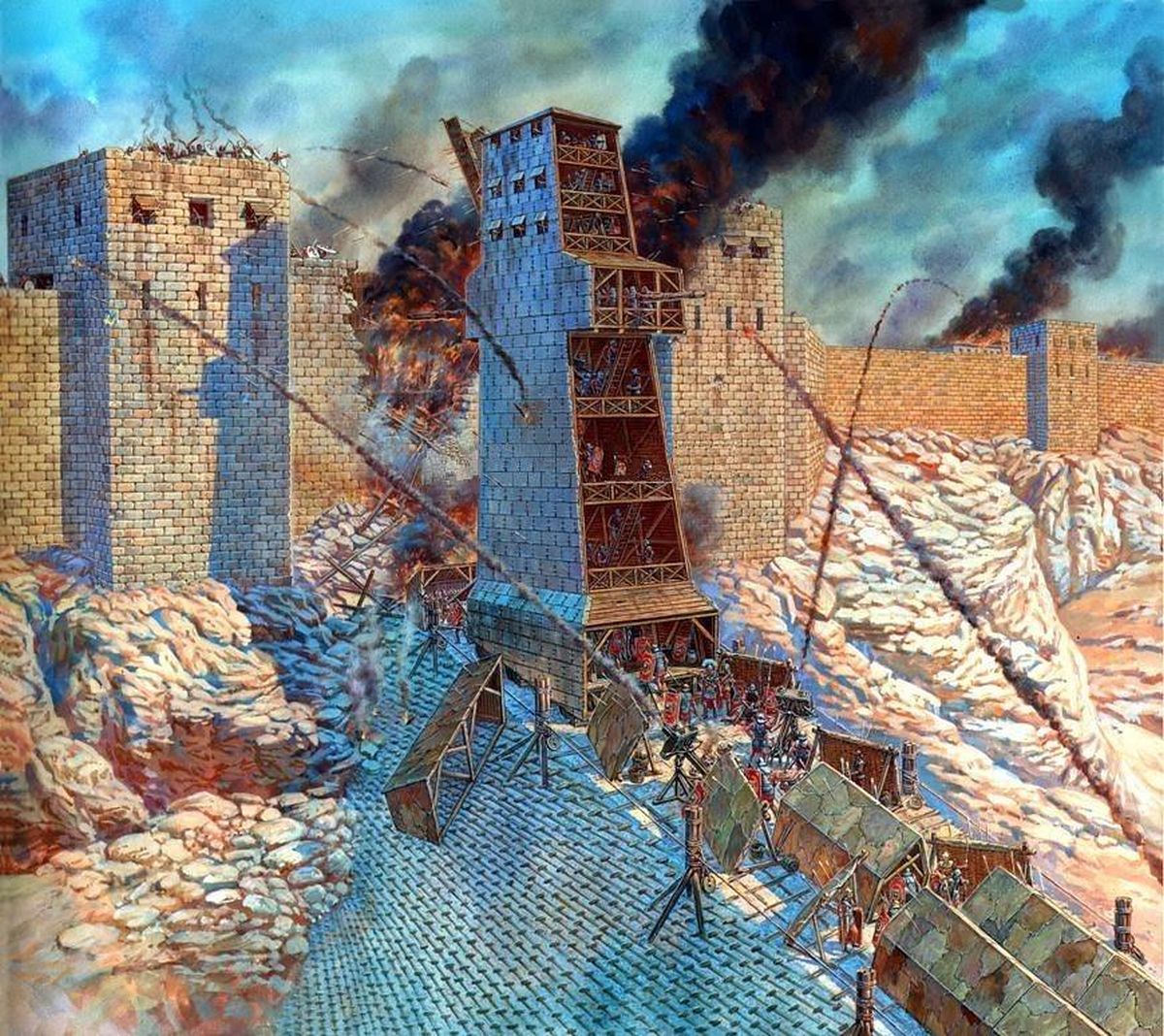

Credit: IMPERIUM ROMANUM
Legacy and Lessons: The Enduring Influence of Roman Siege Warfare
The legacy of Roman siege warfare extends far beyond the ancient world. Medieval armies adopted Roman tactics and technologies, using siege engines to conquer castles and cities. Even today, modern military strategies draw inspiration from the Romans’ ability to combine engineering, strategy, and psychological warfare. The lessons of Roman sieges remind us that innovation and adaptability are key to overcoming even the toughest challenges.
Conclusion: The Timeless Art of Conquest
Roman siege warfare was more than just a military tactic—it was a testament to human ingenuity and determination. From the engineering marvels of siege engines to the strategic brilliance of commanders like Julius Caesar, the Romans left an indelible mark on history. Their sieges were epic events that shaped empires and cultures, proving that the art of conquest is as timeless as it is brutal.
References
- Roman Siege Warfare – World History Encyclopedia
- Roman siege engines – Wikipedia
- Poster, Print Medieval and Roman siege engines and war machines battle in isometric vector ill
- 5 Important Roman Siege Engines | History Hit
- Siege machines of ancient Romans « IMPERIUM ROMANUM
References:
Roman Siege Warfare – World History Encyclopedia – link
Roman siege engines – Wikipedia – link
Poster, Print Medieval and Roman siege engines and war machines battle in isometric vector ill – link
5 Important Roman Siege Engines | History Hit – link
Siege machines of ancient Romans « IMPERIUM ROMANUM – link
Categories: Ancient Warfare, Military History, Roman Empire, War History
Tags: Ancient Warfare, Julius Caesar, Military History, Roman Siege Warfare, Siege Engines
Religion: Ancient Roman Polytheism
Country of Origin: France, Germany, Greece, Israel, Italy, Spain, Tunisia, United Kingdom
Topic: Roman Siege Warfare
Ethnicity: Roman



Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.